Blog

Differences Between On-Grid, Off-Grid, and Hybrid Solar Inverters
Add Date:2025-04-03 Hits: 【Print】Solar inverters are critical components in solar energy systems, converting DC power from solar panels into AC power for use in homes or businesses. Here's a detailed comparison of On-Grid, Off-Grid, and Hybrid Solar Inverters:
Working Principle
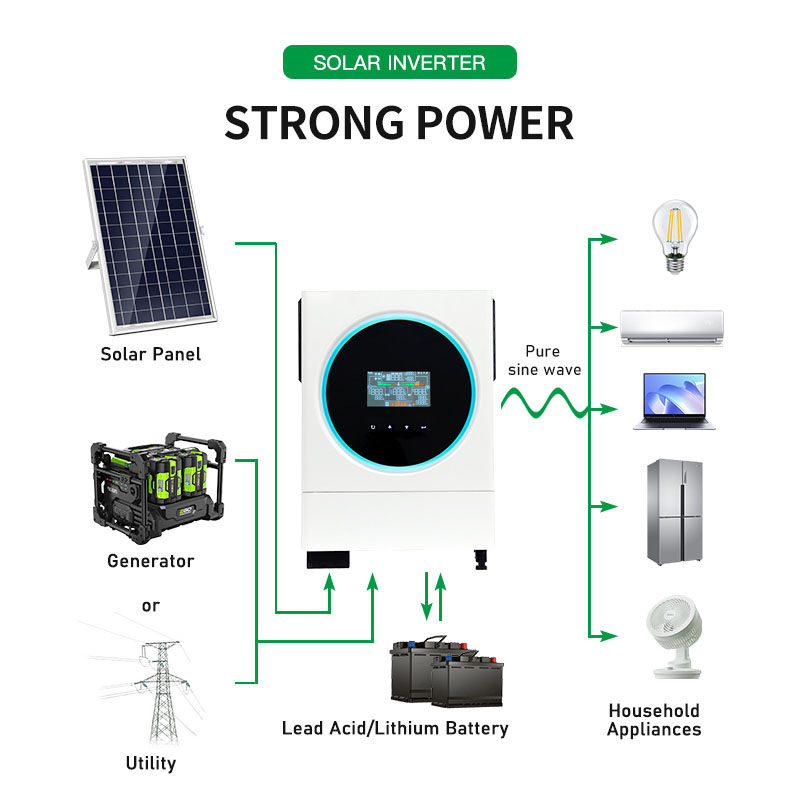
On-Grid Inverter: Converts DC power into AC power and synchronizes it with the public grid. Excess electricity can be fed back into the grid, often earning credits through net metering.
Off-Grid Inverter: Converts DC power into AC power but operates independently of the grid. It typically works with a battery storage system to store excess energy for use when solar generation is low.
Hybrid Solar Inverter: Combines the features of both on-grid and off-grid inverters. It can synchronize with the grid, store excess energy in batteries, and provide backup power during grid outages.
Application
On-Grid Inverter: Ideal for areas with stable grid access, such as urban or industrial regions. It is commonly used in residential, commercial, and large-scale solar power plants.
Off-Grid Inverter: Suitable for remote or rural areas without grid access, such as islands, mountains, or emergency backup systems. It provides complete energy independence.
Hybrid Inverter: Best for areas with unreliable grid access or for users who want to maximize energy independence while maintaining grid connectivity.
Key Features
On-Grid Inverter:
Relies on the grid as a "virtual battery" and does not require energy storage.
Automatically shuts down during grid outages to ensure safety.
Cost-effective and efficient for maximizing solar energy utilization.
Off-Grid Inverter:
Requires a battery storage system to store excess energy.
Provides continuous power supply even during grid outages.
Higher initial investment due to the need for batteries and additional components.
Hybrid Inverter:
Can operate in both grid-tied and off-grid modes, offering flexibility.
Stores excess energy in batteries and can feed surplus power back to the grid.
Provides backup power during grid outages, ensuring uninterrupted supply.
Technical Differences
On-Grid Inverter: Must synchronize with the grid’s frequency and phase to ensure seamless integration.
Off-Grid Inverter: Does not need grid synchronization but must work efficiently with the battery system to maintain stable power output.
Hybrid Inverter: Combines grid synchronization and battery management, offering advanced control and monitoring features.
Cost and Reliability
On-Grid Inverter: Lower initial cost but dependent on grid stability. It cannot provide power during grid outages.
Off-Grid Inverter: Higher initial cost due to battery requirements but offers greater energy independence and reliability, especially in areas with unstable or no grid access.
Hybrid Inverter: Higher initial cost than on-grid inverters but provides the best of both worlds—grid connectivity and energy independence.
Conclusion
The choice between On-Grid, Off-Grid, and Hybrid Solar Inverters depends on your specific needs and location. On-grid inverters are cost-effective for grid-connected areas, off-grid inverters provide energy independence in remote regions, and hybrid inverters offer flexibility and reliability for areas with unreliable grid access or users seeking backup power
 Send Email
Send Email rainny
rainny